Afghanistan is a country with a rich history and culture, but it’s also home to vast untapped natural resources. From minerals to oil and gas reserves, the country is sitting on a wealth of resources that have yet to be fully explored and developed. In this article, we will explore Afghanistan’s untapped natural resources. These resources have the potential to provide significant economic benefits to the country and its people.
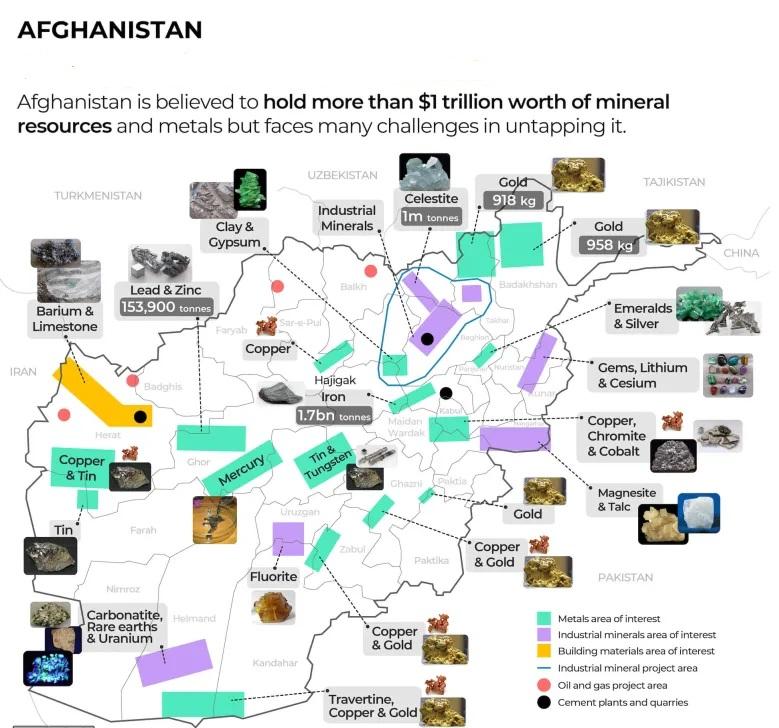
According to research that was issued by Afghanistan’s Ministry of Mines and Petroleum, there are at least one trillion dollars’ worth of undiscovered mineral riches buried deep beneath the ground in Afghanistan, which is one of the poorest countries in the world. It is estimated that the South Asian nation, which has a population of 38 million people, possesses more than 2.2 billion tonnes of iron ore, 1.3 billion tonnes of marble, and 1.4 million tonnes of rare earth minerals.
Geologist Scott Montgomery, who has researched the breadth of Afghanistan’s resources, estimates that it will take the nation a minimum of seven to ten years to develop large-scale mining operations to the point where they become a significant source of revenue.
The Soviet Union and its Eastern European allies carried out exhaustive explorations of the country’s geological resources throughout the 1960s and 1970s. However, as a result of decades of conflict, the majority of the resources stayed underground.
The United States Geological Survey (USGS) and the Afghanistan Geological Survey (AGS) collaborated in 2010 to carry out the most extensive geological survey of the country to date, which resulted in the identification of 24 particular areas of interest (AOI) spread across Afghanistan’s 34 provinces.
Mineral Resources in Afghanistan
Afghanistan is home to a wealth of mineral resources, including copper, iron, gold, and rare earth elements. These minerals have been known for centuries and have been a source of wealth for the country for many years.
In recent years, new deposits have been discovered, and modern exploration techniques have revealed even more mineral resources in the country. Some of the most promising mineral deposits in Afghanistan include the Aynak Copper deposit, the Hajigak Iron Ore deposit, and the Badakhshan Gold deposit.
Iron is the most common of Afghanistan’s important metals, and the country has an abundance of it. It is estimated that Afghanistan’s total iron ore deposit is 2.2 billion metric tons, which places the country among the top 10 countries in terms of extractable iron.
The Hajigak mine, which is situated in the hilly Bamyan province about 130 kilometers (80 miles) west of Kabul, possesses the largest iron ore deposit in the region. The mine’s high-grade ore reserves total 1.7 billion tonnes and range from 63 to 69 percent iron content.
To put that into perspective, it would take 2.2 billion tons of iron ore to build at least 200,000 copies of the Eiffel Tower in Paris. The original tower was built in 1889 out of 7,300 tons of iron and rises at a height of 1,063 feet (324 meters).
It is also believed that the country contains 183 million tons of aluminum resources, the most of which are located in the provinces of Badakhshan and Kandahar. Aluminum, despite its low density, is the world’s second-most-used metal, trailing only iron in popularity.
A total of approximately 2,698 kilograms of gold is believed to be deposited in Afghanistan along two primary gold belts: one runs from Badakhshan to Takhar in the southwest, while the other runs from Ghazni to Zabul in the southwest. With this quantity of gold, it would be possible to issue at least 300,000 gold pound coins, each of which would weigh eight grams.
Building Materials
Afghanistan is ranked as the seventh most hilly country in the world, which makes it difficult to travel around much of the country. The Hindu Kush Himalayas are located in the north-eastern part of the landlocked nation of Afghanistan. These mountains include a variety of minerals and stones, such as marble, limestone, and sandstone, which are all utilized extensively in the building industry.
Marble is a highly adaptable rock that is frequently utilized in the construction industry as well as the art world. There is enough marble in this country to construct 13,000 Washington Monuments, each of which would be 169 meters (555 feet) tall and 17 meters (55 feet) wide. The country produces an amazing 1.3 billion tonnes of the exquisite architectural stone. The province of Nangarhar, which shares a border with Pakistan, is famous for its pink onyx marble, which is considered to be among the most desirable in the region.
Both limestone and sandstone are examples of sedimentary rocks that are widespread and commonly used in the construction industry. Limestone is an important ingredient in many items used around the house, including paint and toothpaste, in addition to being a key part of the cement manufacturing process.
It is estimated that Afghanistan has a total of at least 500 million tonnes of limestone, the majority of which is located in the provinces of Badakhshan, Herat, and Baghlan.
In the past, Afghanistan was considered to be one of the most important sources of lapis lazuli, emeralds, and rubies in the world. The northeastern part of the country is where the vast majority of the country’s gemstones are located.
An estimated 1.4 million tonnes of rare earth minerals can be found in Afghanistan. These minerals include lithium, which is utilized in the production of batteries, and uranium, which is utilized in the production of nuclear fuel. Khanneshin, which is located in the province of Helmand, is home to one of the most significant deposits of rare earth minerals.
Oil and gas reserves in Afghanistan
In addition to mineral resources, Afghanistan also has significant oil and gas reserves. The country is believed to have large oil and gas deposits in the northern and western regions.
Exploration and production activities in the oil and gas sector have been limited in the past due to security concerns and lack of investment. However, with recent developments and improved security, there is a growing interest in the development of these resources. Barite is a colorless mineral that is frequently used by the oil and gas industry in drilling. It is believed that the country possesses 152 million tonnes of barite in its reserves.
Agricultural land in Afghanistan
Afghanistan is also home to fertile agricultural land, with large areas of arable land suitable for agriculture. The country has a rich history of agriculture and has been known for producing high-quality crops such as wheat, maize, and rice.
The potential for agriculture in Afghanistan is significant, and with proper investment and development, the country could become a major agricultural producer. With its favorable climate and fertile soil, Afghanistan has the potential to produce a wide range of crops, including fruits and vegetables, as well as livestock.
Challenges to developing natural resources in Afghanistan
While Afghanistan is home to vast untapped natural resources, there are several challenges to developing these resources. Some of the biggest challenges include security concerns, lack of investment, and a lack of infrastructure.